Refurbished Medical Equipment
Heart Lung Machine
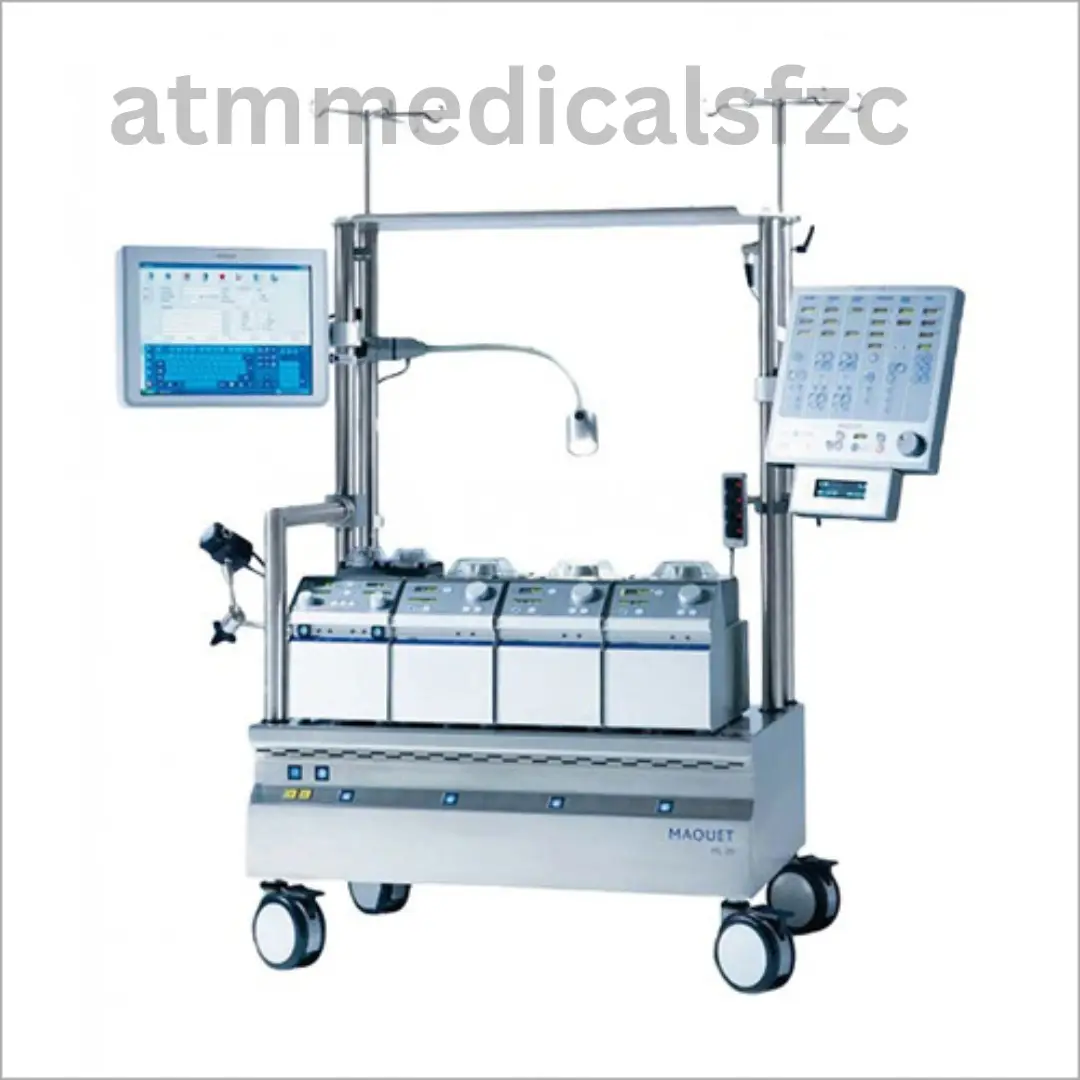
A heart-lung machine, also known as a cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) machine, is a medical device that temporarily takes over the functions of the heart and lungs during cardiac surgeries. It is a critical tool that allows surgeons to perform complex procedures on the heart while maintaining circulation and oxygenation of the patient’s blood.
The heart-lung machine was first developed in the 1950s and has since become an indispensable component of open-heart surgeries. It revolutionized the field of cardiac surgery by providing a means to temporarily halt the heart’s beating and divert the flow of blood away from the heart, allowing surgeons to operate on a still and bloodless field.
Ventilator
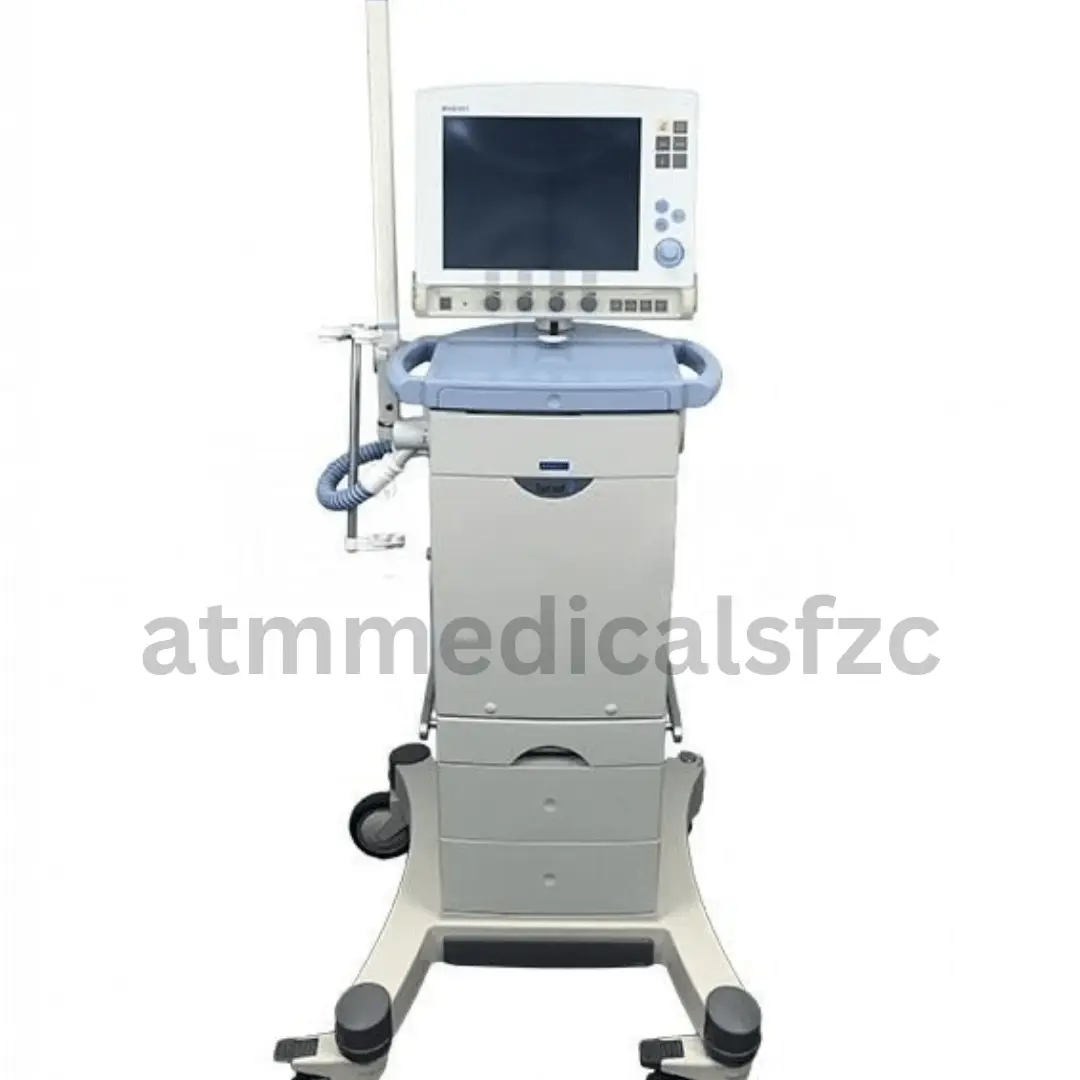
A Ventilator is a machine that helps people breathe. It is also known as a breathing machine or mechanical ventilator. Ventilators are used when a person is unable to breathe on their own, or when they are not breathing enough oxygen into their blood.
There are two main types of ventilators: invasive and noninvasive. Invasive ventilators require a breathing tube to be inserted into the person’s airway. Noninvasive ventilators do not require a breathing tube, and instead use a mask that fits over the person’s face.
Ventilators work by pushing air into the person’s lungs. The amount of air and the pressure of the air can be adjusted to meet the person’s individual needs. Ventilators can also deliver oxygen to the person’s lungs.
Anesthesia
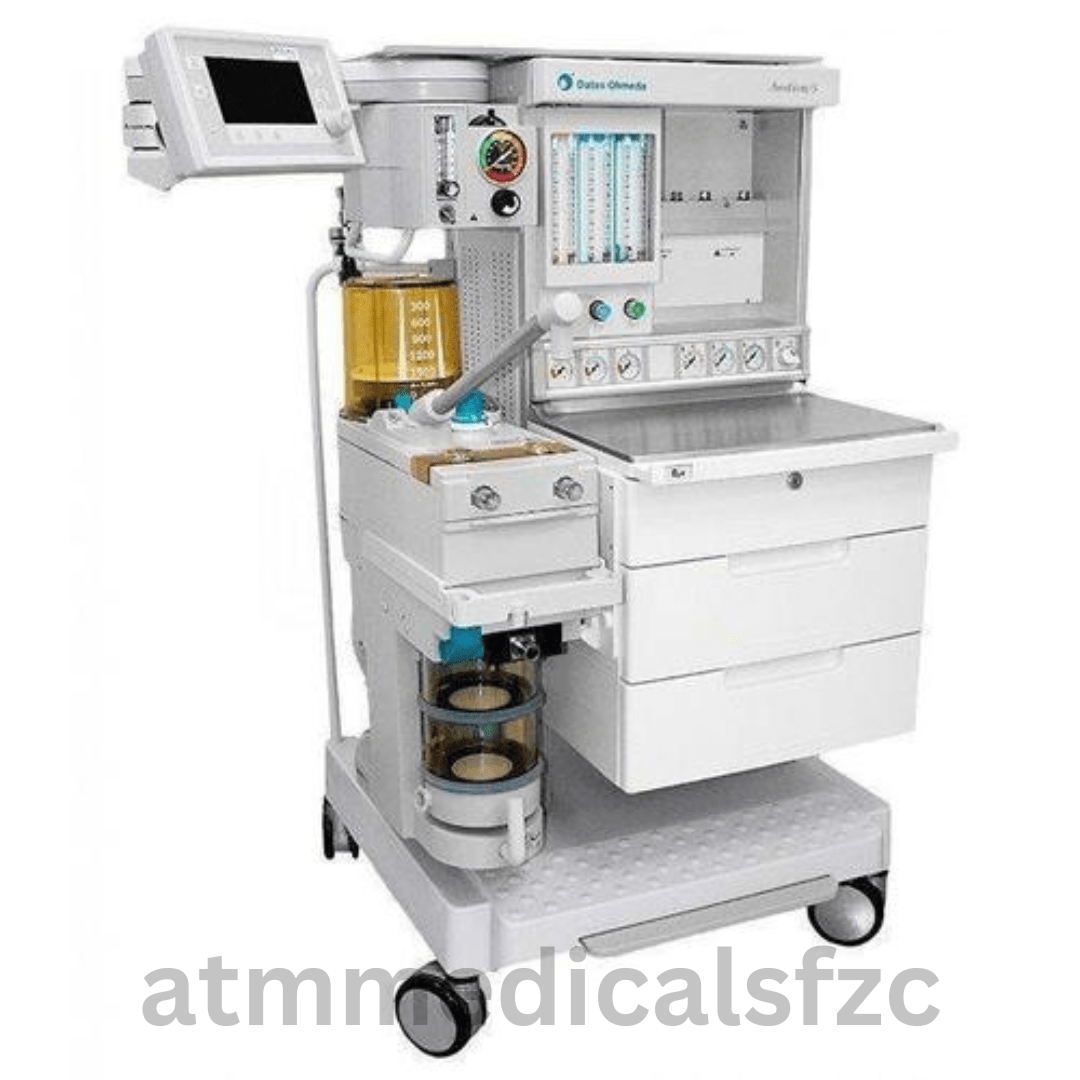
An anesthesia machine is a medical device that supplies a mixture of oxygen, gas, and anesthetic agent to a patient, allowing them to remain unconscious, but breathing, during surgery. It is also used for other procedures, such as childbirth and colonoscopies.
The anesthesia machine has four main functions:
Provides oxygen
Mixes anesthetic gases
Enables patient ventilation
Minimizes anesthesia-related risks
ACT Machine
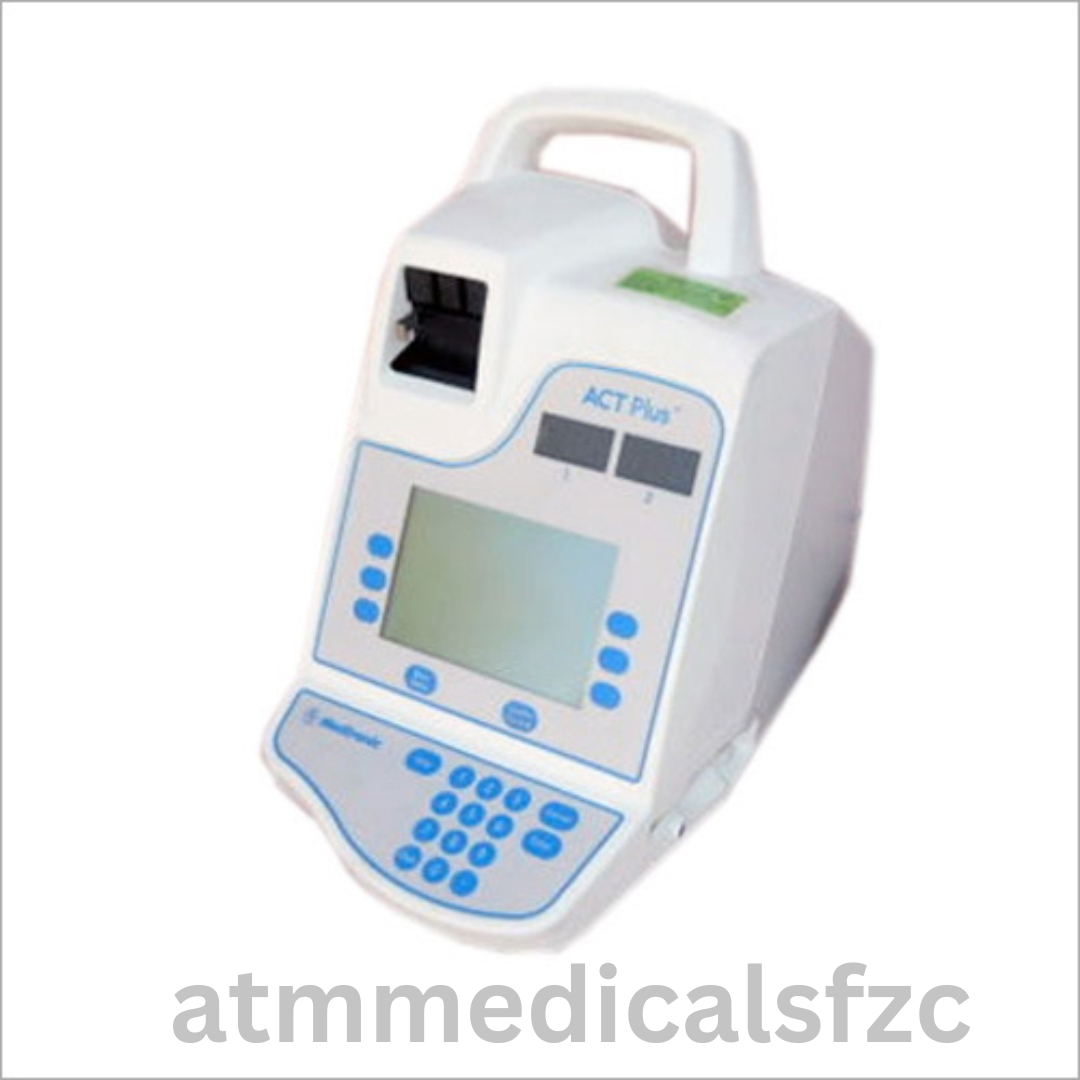
An ACT machine, or Activated Clotting Time machine, is a medical device used to measure the activated clotting time (ACT) of blood. The ACT is a test of how long it takes blood to clot after it has been exposed to a catalyst. This test is used to monitor the effectiveness of heparin therapy, which is a blood thinner used to prevent blood clots.
ACT machines are typically used in hospitals and other healthcare settings. They are small, portable devices that can be easily transported to the bedside. The machine uses a disposable cartridge that contains the reagents and other materials needed to perform the test.
To perform an ACT test, a small sample of blood is drawn from the patient and placed in the cartridge. The cartridge is then inserted into the machine and the test is performed automatically. The results of the test are displayed on the machine’s screen. The normal ACT range is 25-35 seconds.
IABP Machine
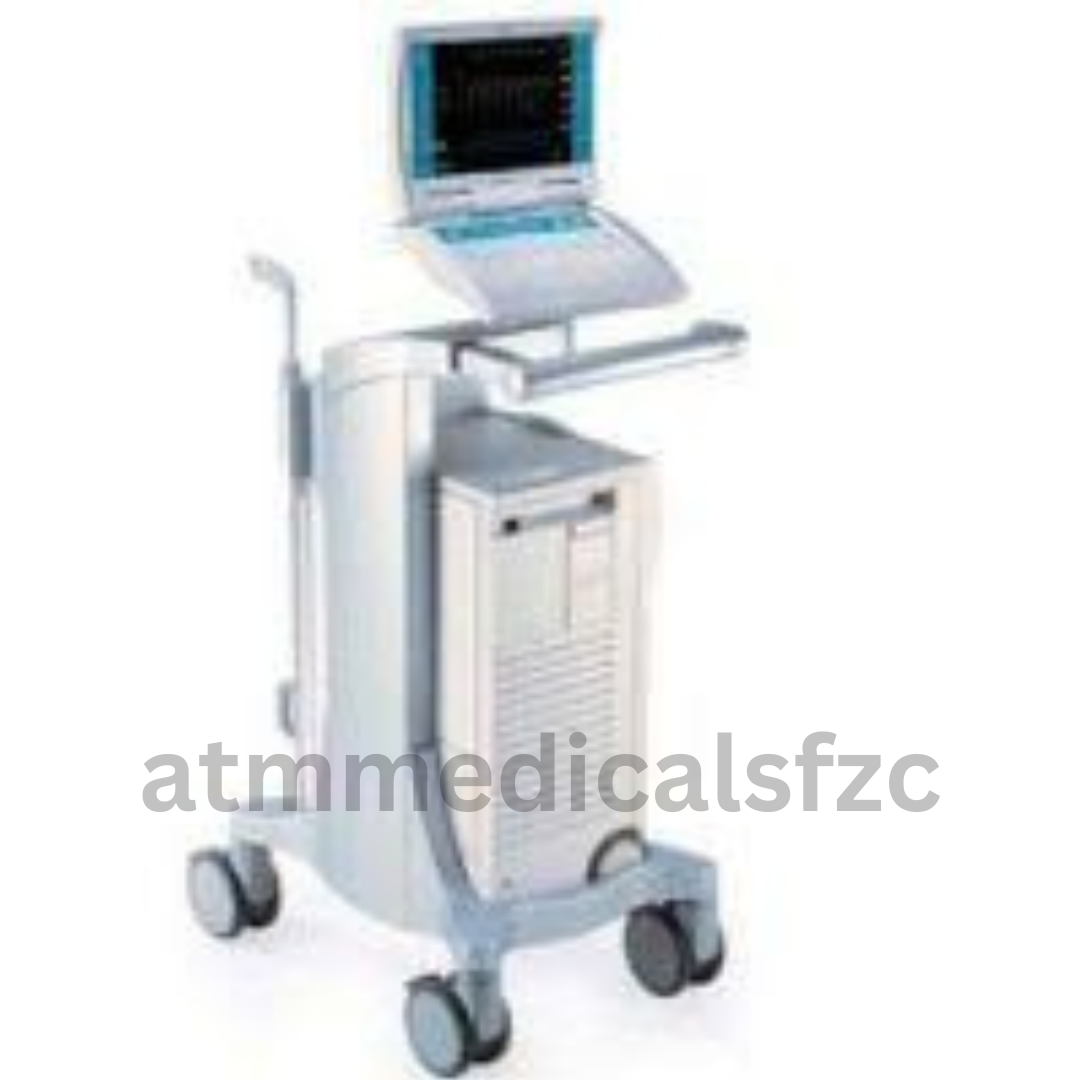
An intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) is a mechanical device that helps the heart pump more blood. It is a long, thin tube called a catheter that has a balloon at the end. The catheter is inserted into a large artery in the leg or groin and threaded up to the aorta, the main artery that carries blood away from the heart.
The balloon is inflated and deflated in a synchronized pattern with the heart’s beats. When the heart contracts, the balloon deflates, which creates space in the aorta. This allows the heart to pump more blood out. When the heart relaxes, the balloon inflates, which helps to push blood back to the heart and to the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle.
Heater Cooler
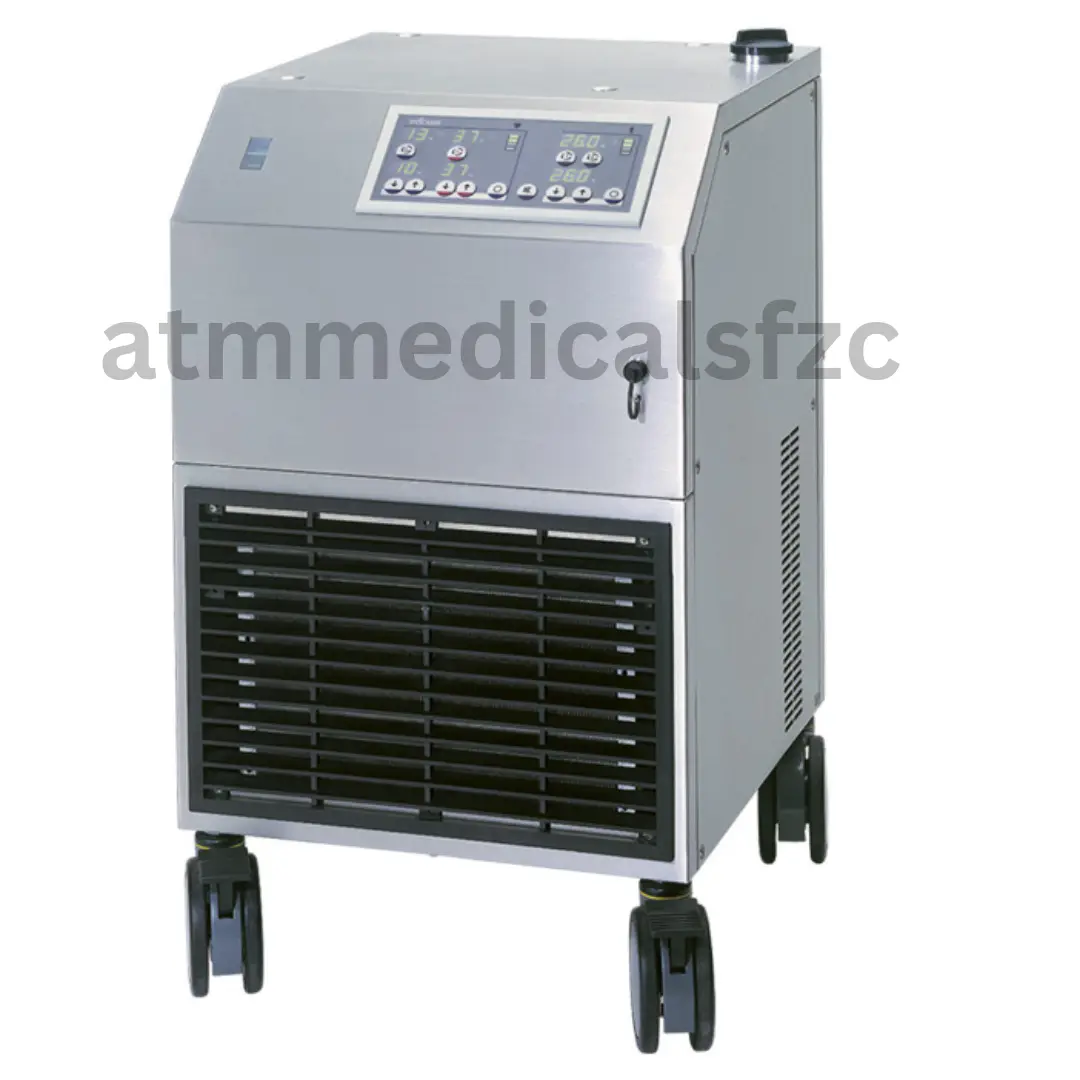

A heater cooler is a device that can both heat and cool the air. It is a versatile appliance that can be used in a variety of settings, including homes, offices, and businesses.
When choosing a heater cooler, it is important to consider the size of the area to be cooled, the climate, and the budget. Evaporative heater coolers are a good option for small areas in mild climates. Forced-air heater coolers are a good option for larger areas or in cold climates.
The benefits of using a heater cooler:
They can save you money on your energy bills.
They are more environmentally friendly than traditional heating and cooling systems.
They can be used to heat and cool the air in all climates.
They are versatile and can be used in a variety of settings.
Monitors
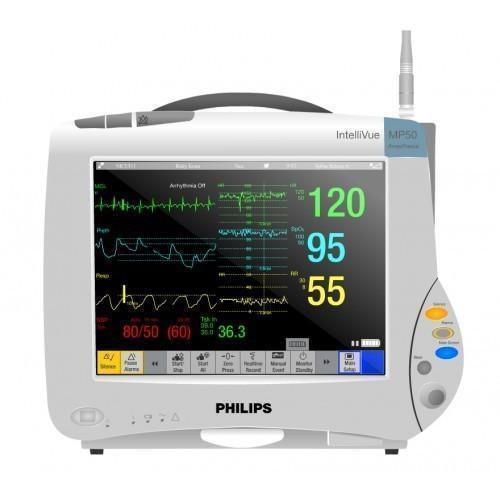
Cardiac monitors are essential medical devices designed to monitor and display the electrical activity of the heart. These monitors play a crucial role in both diagnosing and managing various cardiac conditions by providing real-time information about the heart’s rhythm and other vital parameters. They are widely used in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare settings to ensure prompt and accurate detection of cardiac abnormalities.
Key features of cardiac monitors include:
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG):
Continuous Monitoring:
Parameter Measurement:
Alarm Systems
Portable and Wearable Options
Defibrillators
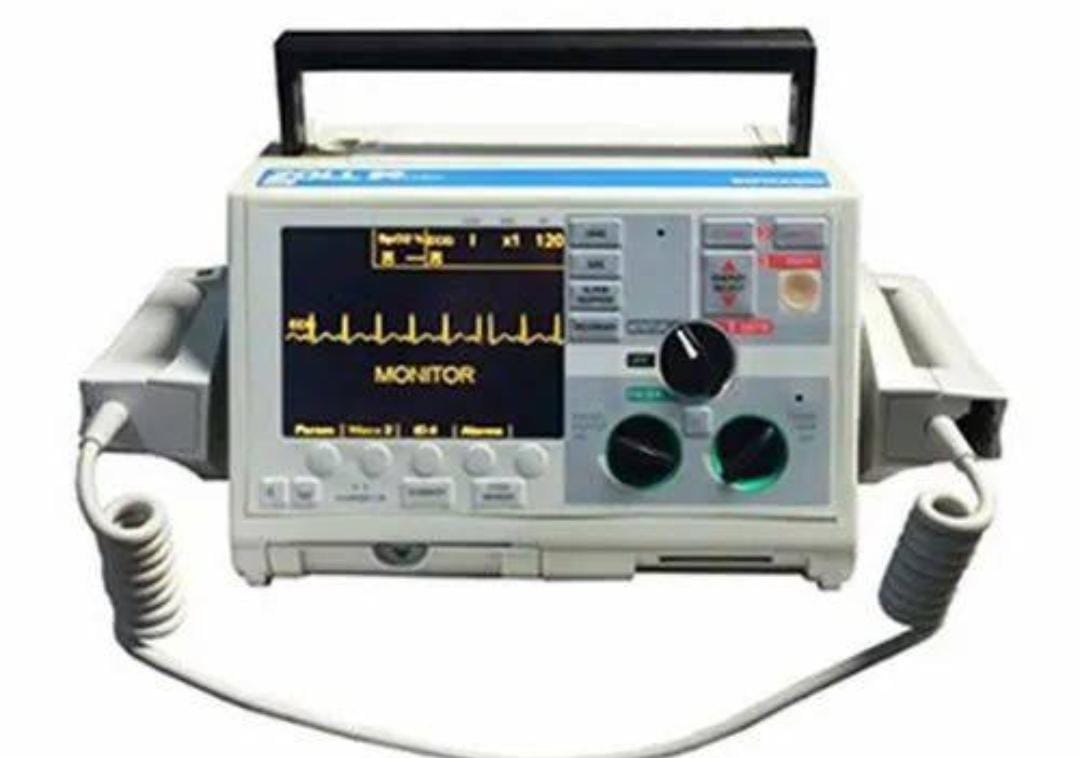
A defibrillator is a life-saving medical device designed to deliver an electric shock to the heart in order to restore its normal rhythm during a cardiac arrest or arrhythmia. Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart’s electrical system malfunctions, leading to a sudden loss of blood flow to the brain and other vital organs. Defibrillators are crucial in these situations, as they can help restart the heart and prevent irreversible damage or death.
There are two main types of defibrillators: automated external defibrillators (AEDs) and manual defibrillators.
Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs): AEDs are portable, user-friendly devices that are often found in public places, such as airports, shopping malls, schools, and sports facilities.
AEDs analyze the heart’s rhythm and deliver a shock only if it detects a specific type of irregular heartbeat called ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia.
Manual Defibrillators: Manual defibrillators are typically used by trained medical professionals, including paramedics, emergency medical technicians (EMTs), and hospital staff.
These devices require the operator to interpret the patient’s cardiac rhythm and manually decide when to deliver a shock.
BIPAP/CPAP
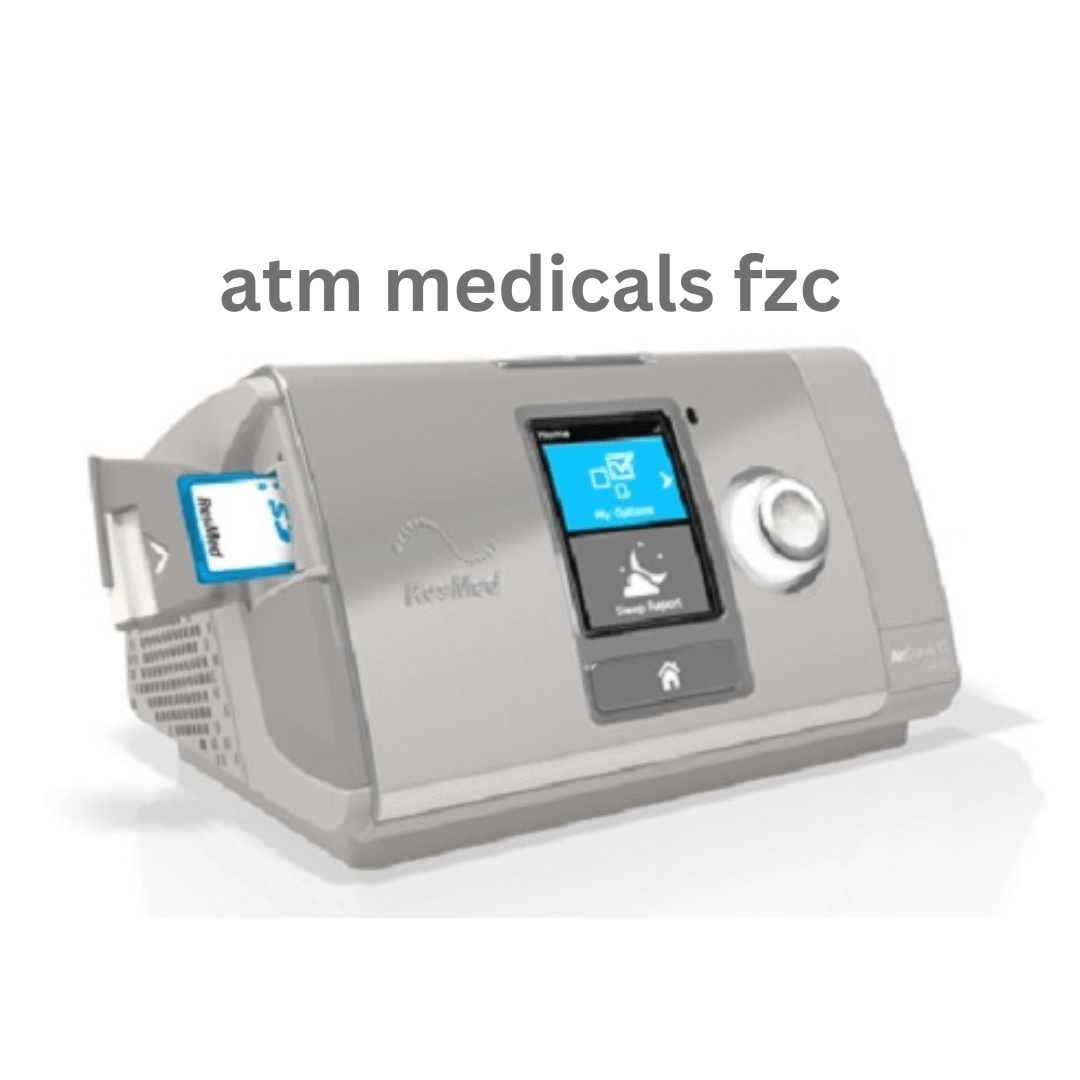
BiPAP, or Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure, is a medical device used in the treatment of respiratory disorders such as sleep apnea and certain types of respiratory failure. It is a non-invasive form of positive airway pressure therapy that helps maintain open airways and assist with breathing.
Here are some key features and aspects of a BiPAP machine
Dual Pressure Levels
Customizable Settings
Adaptability
Patient Synchronization
Data Monitoring
Mask Varieties
